Physical vs Logical Data Structures
In this article, we are going to talk about what physical and logical data structures are.
Physical Data Structures
There are two main physical data structures, those are Arrays and Linked Lists. They are called main physical data structure,s as we can have more data structures by combining and modifying them.
Why do we call array and linked lists physical data structures? We call them Physical Data Structures because they define how the memory is organised and how the memory is allocated. Let’s take a deeper look to each one of these:
Arrays
Arrays are supported by many programming languages, some of them are C, C++, C#, Java and many more. An Array is a collection of contiguous memory locations, that is, all these elements are stored side by side. If we have an array for 6 integers, then all these 6 integers are stored together in memory. They are in one place. Arrays have a fixed size, once they are created, that size cannot be increased or decreased.
This is how an array looks like in memory:
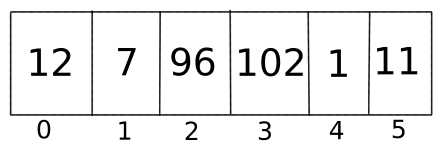
When should we use an Array? If we know the size of the array, basically, if we know the maximum amount of data that will be stored, we should use arrays.
Linked Lists
A Linked List is a dynamic data structure. It is a collection of nodes where each node contains data and a link to the next node in the list. The length of the Linked List can grow and reduce dynamically.
This is how a Linked List looks like:
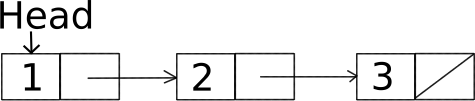
When should we use a Linked List? We should use a linked list when we are not certain of the maximum number of elements that we are going to store.
These two data structures are physical data structures because they define how memory should be organised for storing the elements or data. These are more related to memory.
Logical Data Structures
The following, is a list of logical data structures:
- Stack.
- Queue.
- Tree.
- Graph.
- Hash Table.
Differences between Logical and Physical Data Structures
Physical data structures are made to store data in memory. Now, if in that data in memory we want to perform modifications like inserting, deleting and searching for values, we’d have to go with a Logical Data Structure.
Stack and Queues are Linear Data Structures, whereas Trees and Graphs are non-linear data structures.
The Stack follows the LIFO way of storing data (LIFO stands for Last In First Out), and Queues follow the FIFO (First In First Out). Trees are a non-linear data structure and they are organised in a hierarchy, the graph is a collection of nodes and the links between the nodes.
Types of Data Structures
We can classify data structures into two main types:
- Linear: A linear data structure has data elements arranged in a sequential manner, and each element is connected to its previous and next element, for example, Linked Lists, Stacks and Queues.
- Non-Linear Data Structures: A non-linear data structure has no set sequence of connecting all its elements, and each element can have multiple paths to connect to other elements, for example, trees and graphs.